Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Bae, S.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 104(9), p.4803 - 4818, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:84.26(Materials Science, Ceramics)Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1039 - 1054, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been performed in simulated Boiling Water Reactor water conditions at  288
288 C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at
C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at  12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at
12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at 
 2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 14 Pages, 2017/09
An experimental study on the upward bubbly air-water flows in a vertical large-diameter square duct have been performed by using four-sensor probes. The four-sensor probe were applied in the local measurements at 3 axial positions along the flow direction to obtain interfacial area concentration, 3-D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter. The obtained void fraction, interfacial area concentration, 3-D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter provided valuable insight into the flow structure and will serve as a valuable database to develop the mechanistic models for interfacial area transport equation sources and sinks.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 475, p.71 - 80, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To elucidate the mechanism of irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) in high-temperature water for neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels (SSs), the locally deformed structures, the oxide films formed on the deformed areas, and their correlation were investigated. Tensile specimens made of irradiated 316L SSs were strained 0.1%-2% at room temperature or at 563 K, and the surface structures and crystal misorientation among grains were evaluated. The strained specimens were immersed in high-temperature water, and the microstructures of the oxide films on the locally deformed areas were observed. The appearance of visible step structures on the specimens' surface depended on the neutron dose and the applied strain. The surface oxides were observed to be prone to increase in thickness around grain boundaries (GBs) with increasing neutron dose and increasing local strain at the GBs. No penetrative oxidation was observed along GBs or along surface steps.
Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 89, p.140 - 158, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:89.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)An experimental study was performed on the local structure of upward air-water two-phase flow in a vertical large diameter square duct by using a four-sensor probe. The four-sensor probe method classifying spherical and non-spherical bubbles was applied as a key measurement way to obtain local parameters such as 3-D bubble velocity vector, bubble diameter and interfacial area concentration. Both the local void fraction and interfacial area concentration indicated radial core-peak and wall-peak distributions at low and high liquid flow rates respectively. The 2 components of the bubble velocity vector in the cross-section revealed that there exists a rotating secondary flow in the octant symmetric triangular area and the magnitude of the rotating secondary flow increases with the liquid flow rate. Some of constitutive correlations of drift-flux model and interfacial area concentration are reviewed to study their predictabilities against the present data.
 by K-absorption edge XAFS
by K-absorption edge XAFSOkamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Narita, Hirokazu; Tanida, Hajime*
Journal of Molecular Structure, 641(1), p.71 - 76, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:71.89(Chemistry, Physical)The local structure of molten LaCl was investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure(XAFS) of the La K-edge. The nearest La
was investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure(XAFS) of the La K-edge. The nearest La -Cl
-Cl distance andcoordination number were 2.89
distance andcoordination number were 2.89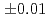
 and 7.4
and 7.4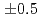 from the curve fitting of the 1st peak in the fourier transform magnitude
from the curve fitting of the 1st peak in the fourier transform magnitude 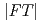 . The coordination number larger than 6 suggests that the local structure of molten LaCl
. The coordination number larger than 6 suggests that the local structure of molten LaCl is not a simple octahedral coordination (LaCl
is not a simple octahedral coordination (LaCl )
) , but 7-fold (LaCl
, but 7-fold (LaCl )
)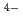 and/or 8-fold (LaCl
and/or 8-fold (LaCl )
)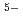 complexes. The 1st La
complexes. The 1st La -La
-La distance, of which correlation was observed as a weak 2nd peak in the
distance, of which correlation was observed as a weak 2nd peak in the 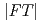 , was evaluated to be 4.9
, was evaluated to be 4.9 . It suggests that the distorted corner-sharing connection of the complex species is predominant in the melt, inontrast with molten YCl
. It suggests that the distorted corner-sharing connection of the complex species is predominant in the melt, inontrast with molten YCl in which the edge-sharing connection of the 6-fold (YCl
in which the edge-sharing connection of the 6-fold (YCl )
) mainly exists.
mainly exists.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(9), p.857 - 860, 2002/09
In order to understand the various phenomena related to the nonlocal transport and structure formation in the plasma, we reviw the topics in the field of (1)laser implosion plasma, (2)space plasma, and (3) magnetic fusion plasma, as a spatial series.
 in LiCl-KCl eutectic
in LiCl-KCl eutecticOkamoto, Yoshihiro; Motohashi, Haruhiko*
Zeitschrift f r Naturforschung, A, 579(5), p.277 - 280, 2002/05
r Naturforschung, A, 579(5), p.277 - 280, 2002/05
The local structure of molten ZrCl in LiCl-KCl eutectic was investigated by using an X-ray absorption fine structure(XAFS) of the Zr K-absorption edge. The nearest Zr
in LiCl-KCl eutectic was investigated by using an X-ray absorption fine structure(XAFS) of the Zr K-absorption edge. The nearest Zr -Cl
-Cl distance and coordination number from the curve fitting analysis were 2.51
distance and coordination number from the curve fitting analysis were 2.51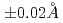 and 5.8
and 5.8 0.6, respectively. These suggest that a 6-fold coordination (ZrCl
0.6, respectively. These suggest that a 6-fold coordination (ZrCl )
) is predominant in the mixture melt.
is predominant in the mixture melt.
 by high-energy X-ray diffraction
by high-energy X-ray diffractionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Ohara, Koji*; Nagata, Hajime*
no journal, ,
KNbO has been a candidate for the end member of a non-Pb ferroelectric materials. We performed local structure analysis of KNbO
has been a candidate for the end member of a non-Pb ferroelectric materials. We performed local structure analysis of KNbO bulk ceramics by high-energy synchrotron X-ray measurements. It has recently established that temperature-driven structural phase transitions in several perovskite ferroelectric materials (PbTiO
bulk ceramics by high-energy synchrotron X-ray measurements. It has recently established that temperature-driven structural phase transitions in several perovskite ferroelectric materials (PbTiO , BaTiO
, BaTiO , and NaNbO
, and NaNbO ) believed to be purely displacive, have a significant order-disorder component. We performed the local structure analysis in a wide-temperature range to observe order-disorder feature of KNbO
) believed to be purely displacive, have a significant order-disorder component. We performed the local structure analysis in a wide-temperature range to observe order-disorder feature of KNbO . The lowest temperature structure of KNbO
. The lowest temperature structure of KNbO is rhombohedral, and we found that the local rhombohedral distortion maintained in the high-temperature cubic phase.
is rhombohedral, and we found that the local rhombohedral distortion maintained in the high-temperature cubic phase.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at  563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Ohara, Koji*
no journal, ,
Atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) is one of the local structure analysis techniques. In SPring-8, one can be performed PDF measurements at bending magnet beamlines owing to its high critical energy. We performed a round robin test by using two bending magnet beamlines for PDF analysis. We concluded that the same data sets can be obtained from both beamlines for the conventional local structure analysis. On the other hand, the results of Rietveld analysis are different owing to the resolution of the incident X-ray beam.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests using compact tension (CT) specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) were performed in simulated BWR environments (at  288
288 C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than
C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than 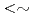 1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than
1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than 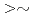 2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.
2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.